Veil of CSR ? CSR stands for
Corporate
Social
Responsibilities whilst different people using different phrases like Corporate responsibility, Corporate citizenship, Sustainability, etc. to describe the same matter.
In the past decade,
CSR became a mainstream approach to business in measuring, managing and reporting its all associated business impacts. It’s defined by
CSRnetwork as how business aligns its values and behaviors with the expectations and needs of stakeholders.
Business for Social Responsibility has added further inputs : achieving commercial success in ways that honor ethical values; respect people, communities & the natural environment when addressing the commercial, legal, ethical and other expectations the society has for business; and making decisions that fairly balance the claims of all key stakeholders.
CSR is a tremendous idea to integrate economic, social and environmental concerns in the business operations of organizations. It demands
wider corporate horizons regarding the position and the role in organizations; and to awaken the sensitivity to the complex and challenging multi-dimensions. It is synonymous with the term “
Triple bottom line” or “
Triple P” ( 3P = Profit, People and Planet ).
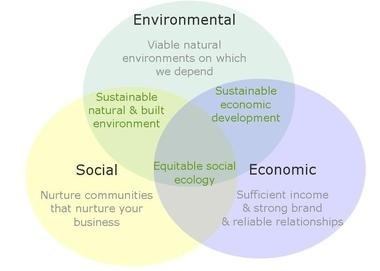
As mentioned, CSR relates to the doctrine of addressing and balancing the needs of different stakeholders. The real challenge emerges on how to
incorporate externalities and
make interface with them in each organizational action, which consumes the company’s capabilities and capacities. The philanthropy serves only a very small portion of CSR’s multi-functions, which include managing risks (e.g. reputation), reducing negative externalities, and accelerating its positive impacts. The awareness & correct understanding of CSR principles are still low, however.
The multitude of initiatives (e.g. Global Compact, Global Reporting Initiative, OECD Guidelines) has started promoting CSR in a voluntary approach. Hence, it is not surprising to see CSR is perceived in different ways. Indeed, its legal development has enforced CSR in a compulsory way, at least in the sense of mandatory CSR reporting and directors’ duties in those developed & some developing countries.
Benefits from practising CSR Throughout the whole development and implementation processes of corporate responsibilities activities, an organization shall ultimately create / add value to its own shareholders and other stakeholders; and to ultimately derive corporate sustainability over a longer span of time, with the following benefits :
(1) Improve traditional & triple bottom line;
(2) Attract investments;
(3) Strategic advantages and creating differentiation;
(4) Engage stakeholders;
(5) Excellent work forces;
(6) Reputation & risk management; and
(7) Incorporate & manage externalities
Important CSR processes Elements for Model CSR practice include (a) Commitment, (b) Stakeholder Engagement, (c) Processes, (d) Standards, (e) Measurable goals and results, (f) Verification & assurance, (g) Disclosure & transparency, and (h) Follow up action.
No success can be anticipated without “blessings” from the Company’s board, CEO and top management who really buy-in, commit and fully support the CSR programs, which involve major business lines and work forces, along the
CSR Route map.
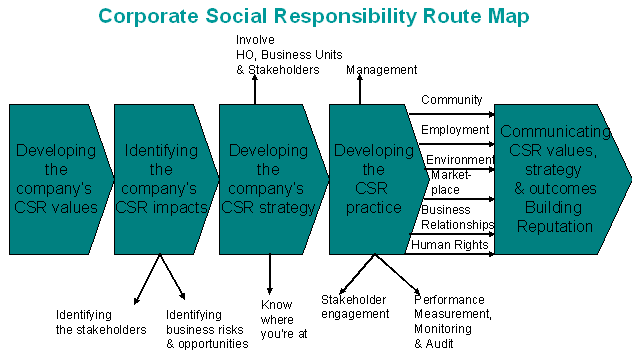
To integrate CSR in an organization’s core business processes means “
changes” and “
consolidation” of different strategies.
Key CSR processes consist of : (1) Understand CSR importance and recognize any possible impacts (good or bad); (2) Seek full commitment from the top; (3) Involve all employees; (4) Set and audit CSR metrics on company-wise (they must be consistent, transparent, material and with data integrity), (5) Make consistent and transparent communication; and (6) Treat CSR as business disciplines (e.g. inclusion of business goals in performance reviews and compensation systems).